Sea Freight Services
 Welcome to CargoMaster, your trusted ocean freight forwarder and global logistics partner. With years of experience in providing comprehensive sea freight solutions, we pride ourselves on delivering reliable and cost-effective sea freight services to destinations worldwide. From door-to-door shipping to specialized logistics, CargoMaster ensures seamless transport for all your cargo needs, making international shipping straightforward and stress-free.
Welcome to CargoMaster, your trusted ocean freight forwarder and global logistics partner. With years of experience in providing comprehensive sea freight solutions, we pride ourselves on delivering reliable and cost-effective sea freight services to destinations worldwide. From door-to-door shipping to specialized logistics, CargoMaster ensures seamless transport for all your cargo needs, making international shipping straightforward and stress-free.
Our extensive network of sea freight carriers and logistics experts allows us to cater to a wide range of requirements, whether you’re shipping containers overseas, transporting heavy equipment, or consolidating shipments for international delivery. With CargoMaster, you can expect personalized service, transparent sea freight quotes, and on-time delivery, no matter the destination.
Experience the difference of working with a dedicated team committed to excellence in ocean freight logistics. At CargoMaster, we simplify international container shipping with innovative solutions, real-time sea freight tracking, and expert guidance every step of the way. Our goal is to provide cost-effective and dependable shipping services that help you stay competitive in today’s global marketplace.

CargoMaster specializes in international sea freight services, offering unparalleled expertise in ocean freight transport and logistics. Our team is well-versed in managing shipments of all sizes, ensuring safe and efficient delivery to over 300 international cities. Whether you’re shipping commercial goods, personal belongings, or industrial equipment, we provide sea freight solutions tailored to your specific needs. With years of proven industry experience, we understand the complexities of international trade and deliver solutions that reduce costs while maximizing efficiency.
Our sea freight services include door-to-door delivery, consolidation, and weekly vessel departures from major Australian ports, including Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, Darwin, Townsville, and Port Hedland. By partnering with leading ocean freight shipping companies, we offer competitive sea freight rates and reliable sea freight tracking to keep you informed throughout the journey. Our strong global network ensures your shipments move seamlessly across borders, no matter the size or destination.
Trust CargoMaster to handle your sea freight forwarding needs with precision and care. Our commitment to excellence ensures that your cargo is delivered on time, every time, making us a preferred choice for global ocean freight logistics. With a focus on reliability and customer satisfaction, we continue to build long-lasting relationships with individuals and businesses who depend on our expertise.

Sydney Melbourne Brisbane Perth Adelaide Canberra Darwin Hobart
20ft and 40ft Containers
 CargoMaster offers flexible container shipping services, including 20ft and 40ft sea freight containers, to meet the diverse needs of our clients. These containers are ideal for transporting goods of various sizes, from small personal shipments to large-scale commercial cargo. Our sea freight carriers ensure secure and efficient transport, whether you’re shipping locally or internationally.
CargoMaster offers flexible container shipping services, including 20ft and 40ft sea freight containers, to meet the diverse needs of our clients. These containers are ideal for transporting goods of various sizes, from small personal shipments to large-scale commercial cargo. Our sea freight carriers ensure secure and efficient transport, whether you’re shipping locally or internationally.
Our services include flat racks, open-top containers, and specialized options for oversized or irregularly shaped cargo. With comprehensive sea freight logistics support, we facilitate seamless international container shipping to destinations across the Middle East, Europe, North America, South America, Africa, and the Asia-Pacific region.
Choose CargoMaster for reliable container shipping services backed by expert knowledge and cutting-edge technology. Our global ocean freight solutions are designed to simplify the shipping process while providing exceptional value and service. International Shipping Container Dimensions Type of Container Inside Dimensions (m) Door Opening (m) Tare Weight (kgs) Volume (cbm) Loading Capacity (kgs) 20' Standard Container 5.92x2.34x2.38 2.29x2.28 1.9 33 22.1 20' Open Top Container 5.92x2.34x2.38 2.29x2.28 2.177 31.6 21.823 20' Reefer Container 5.38x2.24x2.29 2.24x2.12 3.209 24.1 17.111 20' Flatrack 5.94x2.40x2.27 2.56 21.44 40' Standard Container 12.06x2.35x2.38 2.29x2.28 3.107 67.3 27.373 40' Open Top Container 12.064x2.34x2.37 2.29x2.25 4.445 64 26.067 40' Reefer Container 11.21x2.25x2.18 2.22x2.12 4.84 49.3 25.64 40' Flatrack 12.07x2.42x2.10 5.55 25.22 40' High-Cube 12.06x2.34x2.68 2.29x2.25 3.265 75.8 27.215
Self-Pack Containers

Save time and money with CargoMaster’s self-pack container services. This low-cost alternative to traditional removalists allows you to pack your own goods in a 20ft or 40ft shipping container, providing flexibility and control over your move. Our self-pack containers are available from all major Australian cities and can be delivered to most international destinations. With regular sailings and reliable connections, we make overseas moving simple, secure, and cost-effective.
Whether you’re relocating overseas or managing a commercial shipment, our self-pack sea freight services offer convenience and affordability. We provide expert guidance on packing, securing, and preparing your goods for transport, ensuring they arrive safely and intact. This option is ideal for families, students, and businesses seeking a hands-on, budget-friendly shipping solution without compromising reliability.
Contact CargoMaster to learn more about our self-pack international moving containers and discover how we can simplify your overseas cargo shipping experience. Our team is ready to assist with planning, scheduling, and customs clearance support, giving you confidence and peace of mind from start to finish.








 Specialized Freight Services / Break Bulk / Heavy Oversized
Specialized Freight Services / Break Bulk / Heavy Oversized

CargoMaster is a leader in specialized freight services, including break-bulk, out-of-gauge, and heavy oversized cargo shipping. Our team has extensive experience working with industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing, ensuring seamless transport of machinery, equipment, and industrial goods. No matter how complex or challenging the cargo, we design strategies that minimize risk and maximize efficiency.
We collaborate with ocean freight carriers and logistics partners to provide customized solutions for oversized and heavy cargo. From flat racks and open-top containers to specialized handling equipment, CargoMaster’s sea freight logistics ensure your goods are transported safely and efficiently. Our global partnerships allow us to deliver flexible options that meet strict deadlines while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
With our expertise in maritime freight services, we handle every aspect of the process, from planning and documentation to delivery and setup. Trust CargoMaster for reliable and cost-effective ocean freight transport tailored to your unique requirements. Our commitment to precision and customer satisfaction has made us a preferred partner for businesses moving challenging freight worldwide.
Customs Clearance

Navigating customs regulations can be challenging, but CargoMaster simplifies the process with expert customs clearance services. Our team ensures your shipments comply with all necessary regulations, minimizing delays and avoiding unnecessary costs. We work closely with customs authorities and shipping lines, streamlining the process and helping you avoid common pitfalls that can slow down freight movements.
From managing tariff classifications to preparing export documentation, we handle every detail with accuracy and efficiency. Our deep understanding of international trade regulations and sea freight logistics enables us to provide seamless customs clearance for commercial imports, personal goods, and specialized cargo. By keeping up to date with the latest regulatory changes, we help you stay compliant while saving time and money.
Trust CargoMaster for reliable customs clearance services that prioritize compliance and efficiency. With our expertise, your shipments will clear every checkpoint without hassle, ensuring smooth global cargo delivery. We pride ourselves on making the complex world of customs straightforward, giving you confidence and peace of mind with every shipment.
Contact CargoMaster today for a free sea freight quote and discover how our global ocean freight solutions can meet your shipping needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sea freight, and why use it?
Sea freight shipping involves the transportation of goods by sea in a cargo vessel. CargoMaster offers weekly sea freight services from Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide. Sea freight is ideal for goods that do not require urgent delivery, as it is more cost-effective than air freight for larger shipments.
How does sea freight work?
CargoMaster handles all types of sea freight to and from Australia. International sea freight can be collected and consolidated inside shipping containers or consigned as break bulk or out-of-gauge cargo. We also offer a low-cost relocation service for those moving overseas with shipping containers. For more details, call CargoMaster.
What are ocean freight services?
Ocean freight services refer to cargo transported by sea on or inside a cargo ship. These services are available from all Australian capital cities to nearly anywhere in the world. They include transportation by sea container or break bulk cargo. Call CargoMaster for sea freight rates from Australia.
What does sea freight mean?
Sea freight refers to the transportation of cargo by sea on or inside a cargo ship. It is the oldest form of international transportation. CargoMaster is one of Australia’s most trusted sea freight companies.
What are ocean freight charges?
Ocean freight charges, or sea freight charges, are costs associated with moving goods by sea. These include various charges payable at the origin and destination.
Is air freight more expensive than sea freight?
Yes, air freight is more expensive than sea freight. However, air freight is faster and better suited for fragile or valuable cargo.
How much more expensive is air freight than sea freight?
Air freight is significantly more expensive than sea freight due to its faster transportation time. For the best sea and air freight quotes to or from Australia, call CargoMaster.
What are the dimensions of a 20-foot shipping container?
A 20-foot shipping container is approximately 5.9 meters long, 2.3 meters wide, and 2.3 meters high. It offers a cargo capacity of about 30 cubic meters, making it ideal for transporting the contents of a standard three-bedroom home.
What are the dimensions of a 40-foot shipping container?
A 40-foot shipping container measures approximately 12 meters long, 2.35 meters wide, and 2.35 meters high, with a cargo capacity of about 60 cubic meters. It is well-suited for larger shipments, including furniture, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
Can CargoMaster help with shipping vehicles?
Yes, CargoMaster specializes in securely transporting vehicles from Australia. Vehicles are carefully packed into containers using professional blocking and bracing techniques, ensuring they remain safe and undamaged during transit.
How should I pack a container for international shipping?
Proper packing is essential for safe shipping. CargoMaster recommends evenly distributing weight, securing goods with ratchet straps, and protecting furniture by wrapping it in blankets or plastic. To prevent spills when opening, ensure items are packed securely away from the doors. CargoMaster provides expert packing advice to ensure your shipment arrives in pristine condition.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

SAVE TIME SAVE MONEY
Addition Information The international community has established a classification system for easy identification of dangerous goods. These goods fall into nine primary classes, and some classes are further divided to address specific risks. Each class/division has a corresponding label that accurately represents the nature of the hazard. These labels must be attached to the package during transport and remain intact throughout the journey. Take a look at the illustrated examples below to understand how these labels effectively communicate the potential dangers. Under regulations, labels must be clearly visible on the outside of the package and must stay on the package while in transit. You can often find labels printed on most inner packages such as: Below are the 9 hazard labels for the 9 classes of dangerous goods. This includes items such as: These can be transported as: This includes aerosols. Class 2 has 3 divisions: This includes liquids with a boiling point of 35⁰ C or less, or a flash point of 60⁰ C or less such as: These are substances that can spontaneously combust and substances, that when they come into contact with water or emit flammable gases. Class 4 has 3 divisions: These substances are not necessarily combustible on their own but can react dangerously with other substances. Class 5 has 2 divisions: These substances can cause sickness, injury or death if consumed. Class 6 has 2 divisions: These are substances that emit invisible ionising radiation that can be harmful to humans and animals. It can cause objects such as aircraft and equipment to become contaminated if not packaged and handled correctly, such as: These substances can cause irreversible damage if they come into contact with skin and could destroy other freight, or materially damage containers or aircraft. This includes: These are substances and articles which, during air transport, present a danger not covered by other classes. There are 2 types of handling labels – 1 for lithium battery shipments, and another for all other miscellaneous dangerous goods. This class includes: In addition to hazard labels, trained staff must attach handling labels where needed. Staff must use these 4 handling labels with the appropriate hazard labels: This label is used to show that the load cannot be carried on a passenger aircraft. This label is used on liquefied gases, such as the ones in Class 2. This label ensures a load is placed the correct way up and can be used for non-dangerous goods. This label ensures that the load is kept away from the aircraft compass detector unit while being loaded and unloaded. Please Note: The below list does not describe all types of hazardous air cargo (it is not exhaustive and all encompassing). General items listed below may be found in baggage and possibly have hazards that are not immediately apparent. There are strict laws in relation to lodging of hazardous air cargo and compliance with hazardous air cargo regulations. Typical examples of hazardous air cargo INCOTERMS are standard trade terms most commonly used in international freight contracts for sale of goods. It is essential that you are aware of your terms of trade prior to shipment. EXW – EX WORKS (… named place of delivery) FCA – FREE CARRIER (… named place of delivery) CPT – CARRIAGE PAID TO (… named place of destination) CIP– CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO (… named place of destination) DAT – DELIVERED AT TERMINAL (… named terminal at port or place of destination) DAP – DELIVERED AT PLACE (… named place of destination) DDP – DELIVERED DUTY PAID (… named place) MARITIME TERMS FAS – FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP (… named port of shipment) FOB– FREE ON BOARD (… named port of shipment) CFR– COST AND FREIGHT (… named port of destination) CIF – COST INSURANCE AND FREIGHT (… named port of destination) Why is it crucial to verify Bill of Lading details? When is the Bill of Lading Issued? How is the Bill of Lading Compiled? A Contract in Documentation: The Bill of Lading Insight into the Documentation Timeline Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) When exporting to certain countries you will require a Certificate of Free Sale (CFS), also called an export certificate or certificate of export. An Export Certificate confirms in writing that you can sell your goods in the Australian market and that there are no restrictions. The Certificate of Free Sale certifies that you have the approval of relevant authorities to sell your goods in Australia. The overseas purchaser of your products may have problems with customs clearance and registration process’s if you do not provide a CFS when required, your buyer may not be able to import your product into their country. You may need to present this certificate as part of the customs clearance or registration process. A CFS is often requested for products such as: Not all countries require a CFS, the need for a Certificate of Free Sale will depend on your product and your export market. Speak with your buyer to find out if you need a CFS. Where can I get a Certificate of Free Sale? To find out more and apply for a Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) visit: ATA Carnet (Admission Temporary Admission) An ATA Carnet is an international document that permits temporary the temporary entry of commodities into overseas countries. Carnets are used for goods that are intended to be imported for a short period of time, then exported back to the country of origin. It provides exemptions for import duties and taxes. It is most often used for high-value goods imported for specific uses. Typical goods that may be transported under a Carnet: To apply for a Carnet contact The Australian Chamber Of Commerce and Industry Australian Chamber of Commerce and Industry www.australianchamber.com.au/international/certificates-of-origin (ACCI). Phytosanitary Certificate Certificate of Origin (CoO) Note: Always check specific product and market requirements for accurate documentation needs. Certificates of Origin are needed when Origin when Some agreements will allow for a self-certification, while others require a certificate from an authorised body. Self-certification carries a high level of risk and is not recommended for new exporters. There are 2 types of Certificates of Origin A Preferential certificate will assist customs authorities to confirm your compliance with trade agreements made, tariffs and and Rules of Origin. Rules of Origin (ROO) are an agreed set of rules between countries that share a preferential trade agreement, such as a Free Trade Agreement (FTA). ROO set out the criteria for which goods are eligible for free or preferential import tariffs. Typically, they require a product to be entirely produced in a one of the participating countries or have a minimum percentage of the value produced there. They can be complex to understand so speak with your customs broker or freight forwarder or visit the DFAT Free Trade Agreement Portal. Note: If Australia has a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the country you are exporting to you can apply for a Preferential certificate 2. Non-preferential certificates Local governments of most countries issue non-preferential certificates to collect statistical data and ensure you are meeting: Where can I get a Certificate of Origin? To find out more and apply for a Certificate of Origin (COO) visit: For information about the documents needed for specific products check out. CargoMaster ensures a seamless freight experience, combining expertise, accuracy, and compliance for precise cargo transport. Call us at 1300 767 136 for tailored shipping solutions and competitive rates.
(Click the +/- plus/minus symbols to expand/collapse)
FREIGHT TERMS & ABBREVIATIONS
A2A Airport-to-airport A2D Airport-to-door ADV Advise, Advised, Advising
AEAAssociation of European Airlines (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also)
AirlineCompany operating aircraft between steady origin and destination airports Airmail Mail travelling by air Air Operator Company operating aircraft
Airport-to-airportTransport from an airport of origin to an airport of destination
AllotmentAssigned volume on board of a flight / day
AOGAircraft On Ground; materials expedited for repair of a grounded aircraft AP Airport ARR Arrive, Arrived, Arrival ARR Also, a C2K milestone: ARR = cargo and documents arrived at airport of destination ATA Air Transport Association (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also) ATA Actual Time of Arrival ATD Actual Time of Departure Authorisation The commission to a certain person or body to act on behalf of another person or body; the person or body can be authorised e.g., to issue air waybills or to collect freight AVI Live Animal(s) AWB Air Waybill Backlog Amount of goods still to be delivered or received and for which the planned or agreed date has expired BAG Baggage Belly Lower-deck cargo hold of an aircraft BIG Outsized cargo Blocked-space agreement A continuous reservation (allotment) for space at one or more flight / date combinations with an airline Bonded Goods Goods on which the customs duty has not yet been paid, and which therefore, are under the control of customs; usually in a Bonded warehouse. Bonded warehouse A depository for goods on which the customs duty has not been paid; the warehouse proprietor must provide a bond (often in the form of a bank warranty or a mortgage) to the customs authorities as a security for any duties which may not be paid by the customer Booking Request for reservation of space on a flight/day, (to be) confirmed by the airline Break Bulk Agent A forwarder breaking the bulk: taking care of the unpacking and sorting of goods after the flight Breakdown List List of shipments carried in one consolidation (see also: Consolidation Manifest) Broker Person who acts as an agent or intermediary in negotiating contracts; sometimes refers to a forwarder role Bulk Cargo Loose cargo not loaded on an ULD C2K Cargo 2000 (see the “Cargo 2000” page of this website) Cargo Aircraft Aircraft built with the purpose of carrying nothing else than cargo Cargo assembly The separate reception of parcels or packages and the holding of them for later dispatch as one consignment; consolidator role Cargo Disassembly The separation of one or more of the parcels or packages that are part of a consignment for further distribution; break bulk role Carriage Transport; the process of conveying cargo from one point to another Carrier The party responsible for transport of goods from one point to another, this can be for example an airline or a forwarder (as a NVOCC) CASS Cargo Accounts Settlement System CAO Cargo Aircraft Only CC Charges Collect; pay at moment of collection of the goods CCS Cargo Community System; information system integrating the communication between air cargo parties at an airport Certificate of Origin A certificate proving the country of original production of goods; used for customs declaration purposes Charges collect Charges as stated on the air waybill to be collected from the consignee Charges prepaid Charges as stated on the air waybill to be collected from the shipper Claim A written complaint about the execution of a contract of transportation by a carrier, combined with a demand for financial compensation Classifying Assigning the right import classification number to goods as part of the customs declaration process CLR Clear CNEE Consignee COLL Collect, Collected, Collecting COMAT Company Material (non-revenue cargo) Combi Combi Aircraft, combining transport of passengers and cargo on the main-deck Commodity Indication of the type of goods; commodities are coded according to the harmonised system. Commodity code Code used in the Harmonised System for the classification of goods, which are most commonly produced and traded Complaint An official statement from a customer to a carrier about his unhappiness with the service or operation of the service provider Consignee The person or company that is physically and administratively responsible for accepting the goods at final delivery Consolidation A collection of shipments belonging to different shippers travelling to one destination or area to be distributed to several consignees Consolidation Manifest List of shipments carried in one consolidation Consolidation Rates Rates as given by a consolidator / forwarder Consolidator A forwarder consolidating shipments before a flight; these shipments belonging to different shippers and travelling to one destination or area in order to be distributed to several consignees after the flight Courier Company that carries envelopes and parcels up to 75 kg from door to door; air transport is generally outsourced to airlines Courier Rates Rates as given by a courier CPTY Capacity CRN Customs Release Note Customs Agent/Broker (Certified) Party certified to handle the customs clearance on account of importers / exporters Customs invoice (Pro forma) Invoice for import declaration (customs and statistics) purposes, stating the commercial price, added with the costs for freight, insurance and packing etc., terms of delivery and payment Customs value Value of goods to be imported for import declaration (customs and statistics) purposes D2A Door-to-airport D2D Door-to-door Dangerous Goods Goods that can be hazardous for health, flight-safety or materials DAP A C2K key performance indicator: DAP = Delivered as Promised (NFD in full- and on-time statuses are achieved) DEP A C2K milestone: DEP = cargo and documents departed at airport of origin DEPT Department DG Dangerous Goods DGR Dangerous Goods Regulations (IATA) Dimensional Weight (Conversion) Concept adopted by the transportation industry worldwide as a uniform means of establishing a minimum charge for the cubic space a package occupies; the volume is converted into a (higher) weight / price class DIMS Dimensions DIP Diplomatic mail DLV Deliver, Delivered, Delivering DLV Also, a C2K milestone: DLV = cargo and documents delivered to customer (forwarder) DOCS Document(s), Documentation Domestic transport Transport within a country Door-to-door Transport from an initial shipper’s house address to a final consignee’s house address Duty Tax imposed on goods imported from another country EDI Electronic Data Interchange EDIFACT Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport; a specific EDI protocol e-Freight Electronic freight documents project from IATA; e-Freight aims to take the paper out of the air cargo supply chain and -processes and replace it with cheaper, more accurate and more reliable electronic messaging; facilitated by IATA, the project is an industry-wide initiative involving carriers, freight forwarders, ground handlers, shippers and customs authorities Electronic Data
InterchangeThe interchange of electronic data, structured following an agreed protocol, between the automated information system of different parties Embargo An embargo on a certain kind of goods means these goods will not be transported by the airline, often for flight-safety reasons Equipment Materials needed to handle or transport goods ESC European Shippers’ Council (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also) ETA Estimated Time of Arrival ETD Estimated Time of Departure Expediting Forwarding goods (in less than the normal lead time) Expeditor Forwarder FAK Freight All Kinds FAK-Rates Rates for Freight All Kinds FAP A C2K key performance indicator: FAP = Flown as Planned (the complete shipment has flown at or before the last planned flight with a maximum 12-hour delay) FCL Full Container Load FDCA Found Cargo FFM Freight Forwarding Message (electronic) FIATA International Federation of Freight Forwarders Associations (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also)
FLTFlight Forwarder Company specialized in providing door-to-airport transport, arranging connecting air transport and/or airport-to-door transport for parcels and consolidations > 75 kg or up to anything that fits in an aircraft; the air transport is generally outsourced to airlines and sometimes aircraft operators or air charter companies Forwarder network A network existing of different smaller to medium sized forwarding companies all over the world working together Freighter Aircraft built with the purpose of carrying nothing else than cargo
FSUFreight Status Update Fuel Surcharge Surcharge added to the cargo rate to cover the additional costs of increasing fuel-prices; these will generally follow a certain index Full charter Chartering the full available volume of an aircraft or flight/day Full Container Load Container fully loaded, generally with goods belonging to one party Full freighter Aircraft built with the purpose of carrying nothing else than cargo
FWBElectronic air waybill message FWB Also a C2K milestone: FWB = the shipment is booked at the airline, next an electronic air waybill is generated by agent (forwarder) ; this creates the so-called route map in C2K in which all the steps are followed
FYIor Your Information General Cargo Rates Rates for all different kinds of cargo, not falling into a specific handling and/or rate category
GSAGeneral Sales Agent GSF Global Shippers Forum (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also) Handling Agent Agent handling the ramp and/or warehouse cargo operation for an airline Harmonised System A numeric multi-purpose system for the classification of goods with its six digits covering about 5000 descriptions of the products or groups of products most commonly produced and traded, designed for customs purposes, but can also be used for statistics, transport purposes, export, import and manufacturing; the international convention on the HS was established under auspices of the World Customs Organisation in 1983
HaulageInland transport of cargo Haulier Road carrier HEA Heavy Cargo HAWB House Air Waybill House Air Waybill The shipment contract between the end-customer and the forwarder (see the page “Forwarding Out” of this website for further purposes and explanation) Hub Central point in a transport system or network
HUMHuman remains HWB House Waybill IATA International Air Transport Association (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also)
IATA-AgentAn IATA certified agent ICAL Inbound Cargo Action List ICAO International Civil Aviation Organisation (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also) ICE Dry Ice Shipment IN Inches Inco terms Internationally agreed set of standard delivery terms Integrator Carrier integrating different modes of transport to form a door-to-door transport or supply chain; this term mostly refers to the large international express companies whose core business is to carry envelopes and parcels up to 75 kg, often overnight or even same day Intermodal Transport The movement of cargo in a supply chain by more than one mode of transport; for example, road/air or sea/air transport
INVInvoice ISA If Space Available KG Kilos L/C Letter of Credit LCL Less than Container Load Less than Container Load Container partly filled with goods from one party, or an amount of goods that is not sufficient to fill one container and will therefore likely be consolidated LHO Living Human Organs / Blood License, import/export Governmental permit to import / export certain goods under certain conditions Line item Order line, each line on a packing list or invoice to be declared for customs Load factor The extent to which the aircraft (weight-, volume-, ULD-) capacity is efficiently utilized (to generate profit)
LOCLocation Loose cargo/shipments Cargo / shipments not loaded on an ULD Lower Deck The (cargo) deck below the main deck or upper deck of an aircraft LT Local Time Main deck Upper deck; the (cargo) deck above the lower deck of an aircraft Manifest, flight Document listing the air waybills and a specification of the related goods carried on a flight Master Air Waybill The shipment contract between the forwarder and the airline (see the page “Forwarding Out” of this website for further purposes and explanation) MAWB Master Air Waybill MFST Manifest Minimum Rate Rate to cover the basic costs of carrying a shipment MSG Message(s) Network Forwarder A large forwarding company with worldwide branches NFD A C2K milestone: NFD = cargo and documents ready for pick-up at airline (handler), the customer (forwarder) is notified
NNDNotice of Non-Delivery NON-IATA Airline or agent that is not a member of IATA Nose loading Loading cargo through the cargo door in the nose of an aircraft Notify address Address of a party other than the consignee to be notified of arrival of the goods Notify party Party other than the consignee to be notified of arrival of the goods NOTOC Notification To Captain; list for the captain of the aircraft with goods carried on board N-Rates Rates for shipments with weights up to 45 kg NVOCC Non-Vessel Operating/Owning Cargo Carrier; in case of Air Cargo a Carrier (e.g., a Forwarder or Consolidator) who issues Air Waybills for the carriage of cargo on aircraft which he does not operate or own
OAGOfficial Airlines Guide OB On Board Oversized Cargo Cargo that exceeds the dimensions of an ULD
PackagePacked piece of cargo Packing list A list for customs declaration and consignment purposes stating number and kinds of packages being shipped, totals of gross, legal, and net weights of the packages, marks and numbers on the packages, contents and part-/serial numbers Pallet A (standardized) platform on which goods can be stacked for transport or warehouse handling purposes Pallet, aircraft A (standardized) platform on which goods can be stacked for air transport purposes Pallet net A net used to secure the cargo on the aircraft pallet Parcel Package Part charter Chartering of a part of the available volume on an aircraft or flight/day Part shipment Part of a shipment that travels on a different flight and/or day than the rest of the shipment due to available capacity with the airline
PAXPassenger(s) Payload The (cargo) load that can be carried by an aircraft (to generate revenue) PC Piece(s) PER Perishable Cargo PFI Pro Forma Invoice POA Proof Of Acceptance; legal proof a shipment has been accepted by a party POD Proof Of Delivery; legal proof a shipment has been delivered by a party POD Place Of Delivery PP Charges Prepaid PPD Prepaid Pre-alert Message stating the current and or expected status of the goods Principal The customer ordering the transport or related services
PSHPart Shipment QNTY Quantity Q-Rates Rates with a quantity discount RCF A C2K milestone: RCF = cargo has arrived in the cargo bay at final destination; cargo and airwaybill are administratively received in the system
RCPTReceipt, Reception RCS A C2K milestone: RCS = cargo and documents are received ‘Ready for Carriage’ and accepted by airline (handler) Ready For Carriage (By Air) The goods are correctly packed and labelled, and customs cleared, with the right documents attached Ready For Transport (By Road) The goods are correctly packed and labelled, with the right documents attached RFC Ready For Carriage RFT Ready For Transport Routing The path that is (to be) followed by the goods from shipper to consignee
RUSHRRush Reply SASPO As Soon As Possible SAWB Substitute Air Waybill Security Surcharge Surcharge added to the cargo rate to cover the additional costs of the increasing number of security checks and related administration that are legally required by the authorities Shipper The person or company that is physically and administratively responsible for shipping the goods; for an airline in most cases a forwarder will be the shipper, for a forwarder the shipper is a third party, for example a trading company, a manufacturer, etc. Shipper’s Letter of Instruction Document issued by the shipper to instruct and authorize the forwarder to forward and declare goods on his behalf; contains all shipment details needed to facilitate these services
SHPMNTShipment Side loading Loading cargo through a cargo door in the side of an aircraft Skid Pallet S/L Short Loaded SLI Shipper’s Letter of Instruction SSPD Short Shipped; stayed behind TACT The Air Cargo Tariff; publication of official airline tariffs TBA Time Before Arrival TBD Time Before Departure TEMP Temperature TIACA The International Air Cargo Association (see the page “Interest Organisations” of this website also) TILNA Tilting Not Allowed TILTA Tilting Allowed Time Slot The agreed time to collect or deliver goods Tonne Kilometre One tonne (1000 kg or 2204.6 lb) metric flown one kilometre; productivity indicator TRA Transit Tracing Retrieving (information on) the status of goods and documents Tracking Regular checking on the status of goods and documents Track & Trace Automated regular retrieval of (information on) the status of goods and documents and checking these against the agreed norms Transfer cargo Transfer of cargo from one flight to another Transition / Transit cargo Transfer of cargo from one flight to another TRM Transfer Manifest TTL Total ULD Unit Load Device ULD, contoured Unit Load Device shaped to exactly fit in an aircraft UNACC Unaccompanied Unit Load Device Standardized air cargo loading equipment (pallet, container) Upper deck Main deck; the (cargo) deck above the lower deck of an aircraft VAL Valuable cargo VAT Value Added Tax VOL Volume Volume charge Air transport charge based on the volume of goods instead of the actual weight (see “Dimensional Weight” and “Weight charge” also) VUN Vulnerable cargo Weight charge Air transport charge based on the actual weight of the goods (see “Dimensional Weight” and “Volume charge” also) Weight & Balance Management of the weight and allocation of cargo, passengers and fuel for a flight
W/HWarehouse XPS Priority Small Package XS In Excess Yield management The process of maximising the contribution (revenue) of the (transport & handling) network, equipment, infrastructure and resources
SHIPPING CONTAINER DIMENSIONS

20 ft Standard Dry (8'6" x 8' x 20')
Weight: 4500lbs
Max Gross Weight: 66,139lbs
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 19′ 5″
Width: 7′ 8-⅛”
Height: 7′ 9-⅝”
Door Opening:
Width: 7’ 8-½”, Height: 7’ 5-¾”40 ft Standard Dry (8'6" x 8' x 40')
Weight: 8500lbs
Max Gross Weight: 66,139lbs
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 39′ ⅜”
Width: 7′ 8-⅛”
Height: 7′ 9-⅝”
Door Opening:
Width: 7’ 8-½”, Height: 7’ 5-¾”

40 ft High Cube (9'6" x 8' x 40')
Weight: 8750 lbs
Max Gross Weight: 68,008lb
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 39′ 4”
Width: 7′ 7”
Height: 8′ 9″
Door Opening: Width:
7’ 8″‘, Height: 8’ 5”Dimensions of 20ft Flat Rack Container
Internal length 5.94 m / 19.5 ft
Internal width 2.35 m / 7.7 ft
Internal height 2.35 m / 7.7 ft
Tare weight 2,360 kg / 5,203.8 lbs
Payload capacity: 30,140 kg / 66,458.7 lbs
Cubic capacity 32.7 m³ / 1,154.3 cu ft

Dimensions of 40ft Flat Rack Container
Internal length 12.13 m / 39.8 ft
Internal width 2.40 m / 7.9 ft
Internal height 2.14 m / 7 ft
Tare weight 5,000 kg / 11,025 lbs
Payload capacity: 40,000 kg / 88,200 lbs
Cubic capacity 62.2 m³ / 2,195.7 cu ft
SHIPPING CONTAINER DIMENSIONS

20 ft Standard Dry (8'6" x 8' x 20')
Weight: 4500lbs
Max Gross Weight: 66,139lbs
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 19′ 5″
Width: 7′ 8-⅛”
Height: 7′ 9-⅝”
Door Opening:
Width: 7’ 8-½”, Height: 7’ 5-¾”40 ft Standard Dry (8'6" x 8' x 40')
Weight: 8500lbs
Max Gross Weight: 66,139lbs
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 39′ ⅜”
Width: 7′ 8-⅛”
Height: 7′ 9-⅝”
Door Opening:
Width: 7’ 8-½”, Height: 7’ 5-¾”

40 ft High Cube (9'6" x 8' x 40')
Weight: 8750 lbs
Max Gross Weight: 68,008lb
Interior Dimensions:
Length: 39′ 4”
Width: 7′ 7”
Height: 8′ 9″
Door Opening: Width:
7’ 8″‘, Height: 8’ 5”Dimensions of 20ft Flat Rack Container
Internal length 5.94 m / 19.5 ft
Internal width 2.35 m / 7.7 ft
Internal height 2.35 m / 7.7 ft
Tare weight 2,360 kg / 5,203.8 lbs
Payload capacity: 30,140 kg / 66,458.7 lbs
Cubic capacity 32.7 m³ / 1,154.3 cu ft

Dimensions of 40ft Flat Rack Container
Internal length 12.13 m / 39.8 ft
Internal width 2.40 m / 7.9 ft
Internal height 2.14 m / 7 ft
Tare weight 5,000 kg / 11,025 lbs
Payload capacity: 40,000 kg / 88,200 lbs
Cubic capacity 62.2 m³ / 2,195.7 cu ft
SEA FREIGHT CONTAINER OPTIONS
Type of Container Inside Dimensions (m) Door Opening (m) Tare Weight (kgs) Volume (cbm) Loading Capacity (kgs) 20' Standard Container 5.92x2.34x2.38 2.29x2.28 1.9 33 22.1 20' Open Top Container 5.92x2.34x2.38 2.29x2.28 2.177 31.6 21.823 20' Reefer Container 5.38x2.24x2.29 2.24x2.12 3.209 24.1 17.111 20' Flatrack 5.94x2.40x2.27 2.56 21.44 40' Standard Container 12.06x2.35x2.38 2.29x2.28 3.107 67.3 27.373 40' Open Top Container 12.064x2.34x2.37 2.29x2.25 4.445 64 26.067 40' Reefer Container 11.21x2.25x2.18 2.22x2.12 4.84 49.3 25.64 40' Flatrack 12.07x2.42x2.10 5.55 25.22 40' High-Cube 12.06x2.34x2.68 2.29x2.25 3.265 75.8 27.215
HAZARD LABELS FOR DANGEROUS GOODS (DG)
Hazard Labels for
Dangerous Goods (DG)Class 1 Explosives

Class 2 Gases

Class 3 Flammable liquids

Class 4 Flammable solids

Class 5 Oxidising substances and organic peroxides

Class 6 Toxic and infectious substances

Class 7 Radioactive materials

Class 8 Corrosives

Class 9 Miscellaneous
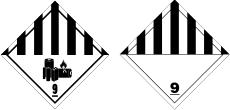
Handling labels
Cargo aircraft only

Cyrogenics

This way up

Magnetised material

HIDDEN DANGEROUS CARGO
Engines (contain fuel and that are not cleaned, purged and sealed)
Mining equipment
Magnets
Pressurised containers
Passenger baggage (containing flammable gas or liquid lighter refuel. camping stove cylinders
Photographic Supplies
Expeditionary equipment
Vaccines
Solvents, adhesives
Pesticides
Dental apparatus
Machinery parts
Frozen foods (packed in solid dry ice)
Dry Ice
Tool Boxes (compressed gases, aerosols)
Electrical equipment
Diving equipment
Pharmaceuticals
Switches in electrical equipment
Toys (made of cellulose)
Refrigerators (may contain gases or chemicals)
Swimming pool chemicals
Pressurised containers
Engines (contain fuel and that are not cleaned, purged and sealed)
Mining equipment
Diagnostic specimens
Thermometers (containing mercury)
Frozen Embryos
Ammunition
Swimming pool chemicals
Aerosols
Compressed non-flammable gas
Batteries
Breathing Apparatus
Frozen foods (packed in solid dry ice)
Motor Vehicle parts
Chemicals
INCOTERMS
The Seller’s only responsibility is to make the goods available at the Seller’s premises. The Buyer bears full costs and risks of moving the goods from there to destination.
The Seller delivers the goods, cleared for export, to the carrier selected by the Buyer. The Seller loads the goods if the carrier pickup is at the Seller’s premises. From that point, the Buyer bears the costs and risks of moving the goods to destination.
The Seller pays for moving the goods to destination. From the time the goods are transferred to the first carrier, the Buyer bears the risks of loss or damage.
The Seller pays for moving the goods to destination. From the time the goods are transferred to the first carrier, the Buyer bears the risks of loss or damage. The Seller, however, purchases the cargo insurance.
The Seller delivers when the goods, once unloaded from the arriving means of transport, are placed at the Buyer’s disposal at a named terminal at the named port or place of destination. “Terminal” includes any place, whether covered or not, such as a quay, warehouse, container yard or road, rail or air cargo terminal. The Seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to and unloading them at the terminal at the named port or place of destination.
The Seller delivers when the goods are placed at the Buyer’s disposal on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the names place of destination. The Seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to the named place.
The Seller delivers the goods -cleared for import – to the Buyer at destination. The Seller bears all costs and risks of moving the goods to destination, including the payment of Customs duties and taxes.
The Seller delivers the goods to the origin port. From that point, the Buyer bears all costs and risks of loss or damage.
The Seller delivers the goods on board the ship and clears the goods for export. From that point, the Buyer bears all costs and risks of loss or damage.
The Seller clears the goods for export and pays the costs of moving the goods to destination. The Buyer bears all risks of loss or damage.
The Seller clears the goods for export and pays the costs of moving the goods to the port of destination. The Buyer bears all risks of loss or damage. The Seller, however, purchases the cargo insurance.
EXPORT DOCUMENTATION
An Overview of Bills of Lading: Ensuring Precision in Shipping
The Bill of Lading meticulously captures the smallest shipment details, providing an exact representation of your cargo. This document is pivotal for identifying your shipment and becomes invaluable in dispute scenarios, especially when handling liability claims for damaged, lost, or delayed shipments.
As a specialist in international shipping and freight, CargoMaster places utmost importance on accuracy in shipping dates, marks, and cargo descriptions when issuing the Bill of Lading. Adhering to maritime regulations, CargoMaster ensures precise details, recognising the significance of the date on the Bill of Lading, marking the enforcement of the shipment contract.
The compilation of a Bill of Lading involves several checks within the export documentation flow. Freight Forwarders like CargoMaster play a crucial role, ensuring accurate details such as container and bolt seal numbers, vessel information, weights, pieces loaded, and voyage numbers. While Bills of Lading are typically issued after the vessel sails, special requests may lead to earlier issuances.
Functioning as a contract between the International Shipping Company and the cargo shipper, the Bill of Lading mirrors other contractual agreements, like a residential tenancy agreement. To meet international standards, Bills of Lading must align with conventions such as The Hague Rule, Hague-Visby Rule, Hamburg Rule, and The Carriage of Goods by Sea Act Australia 1991.
Disputes regarding Bill of Lading issues primarily emerge in cargo exportation. The export documentation flow involves meticulous coordination, ensuring the timely gathering of information from various sources. CargoMaster, handling machinery and out-of-gauge cargo, faces additional documentation requirements for compliance with international regulations.International Freight Certificates: Navigating Export Documentation
A crucial document confirming the approval to sell goods in Australia, essential for customs clearance and import processes in certain overseas markets.
Facilitates the temporary entry of goods into foreign countries, providing exemptions for import duties and taxes. Commonly used for high-value goods at exhibitions, trade shows, motorsports, and audiovisual production.
Required for regulated commodities like plants and plant products, certifying compliance with quarantine regulations and the absence of pests.
Phytosanitary Certificates available from the Department of Agriculture, Water and Environment.
Government-certified or authorised entity-issued document confirming the origin of commodities, essential for Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and customs clearance.
International Logistics Experts

Worldwide |

Sea Freight LCL |

Sea Freight FCL |

Weekly Shipping |
International Freight Routes

|

|

|

|
Thank-you for contacting us, we appreciate the opportunity. If your shipment relates to air freight or less than a container load of sea freight.
Please include the weight and dimensions of each piece in your request. We look forward to working with you, please feel free to call at any time.
Call: 1300 767 136





